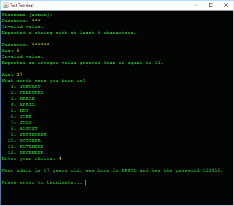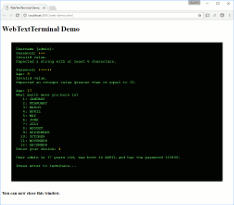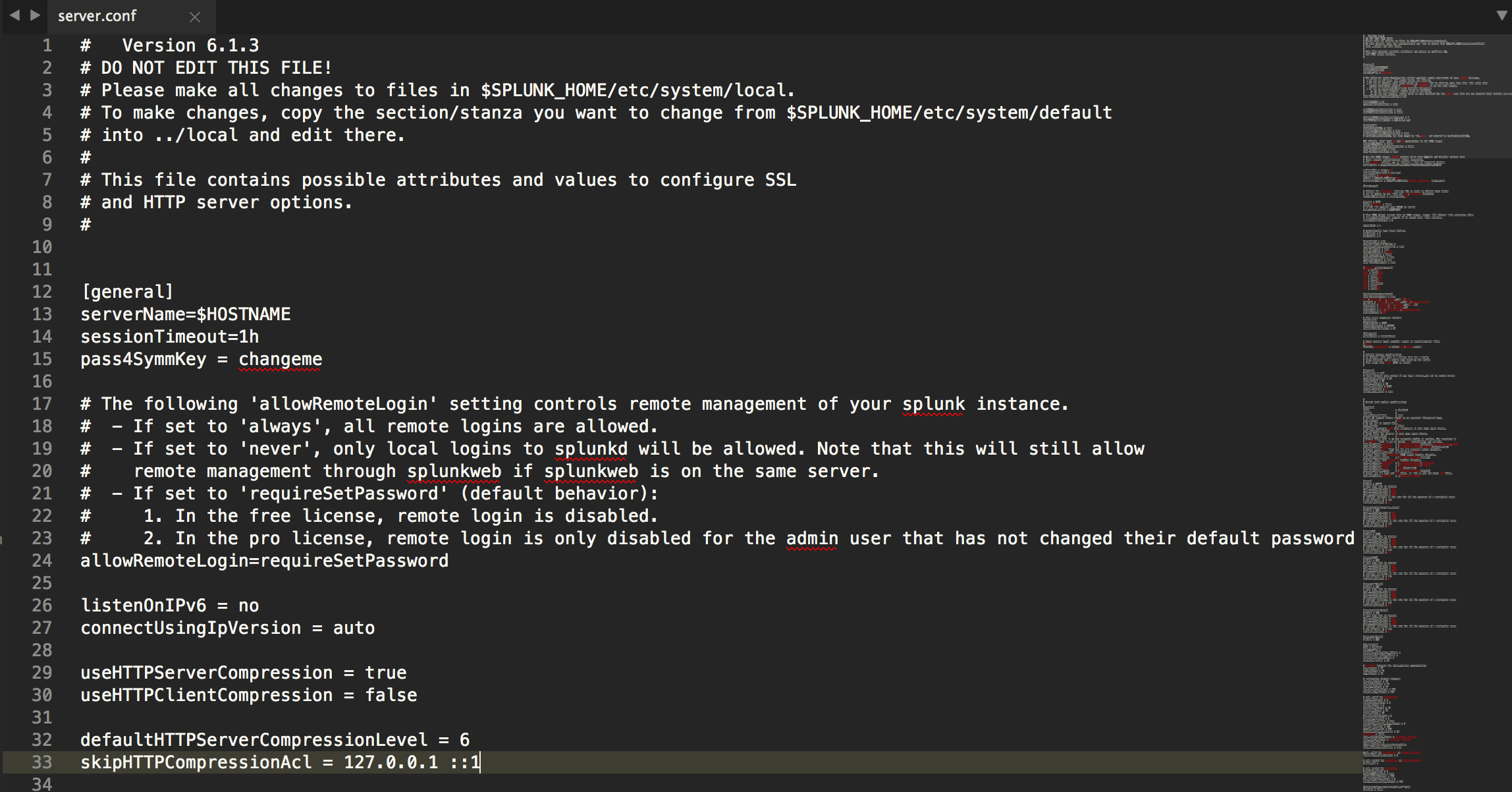
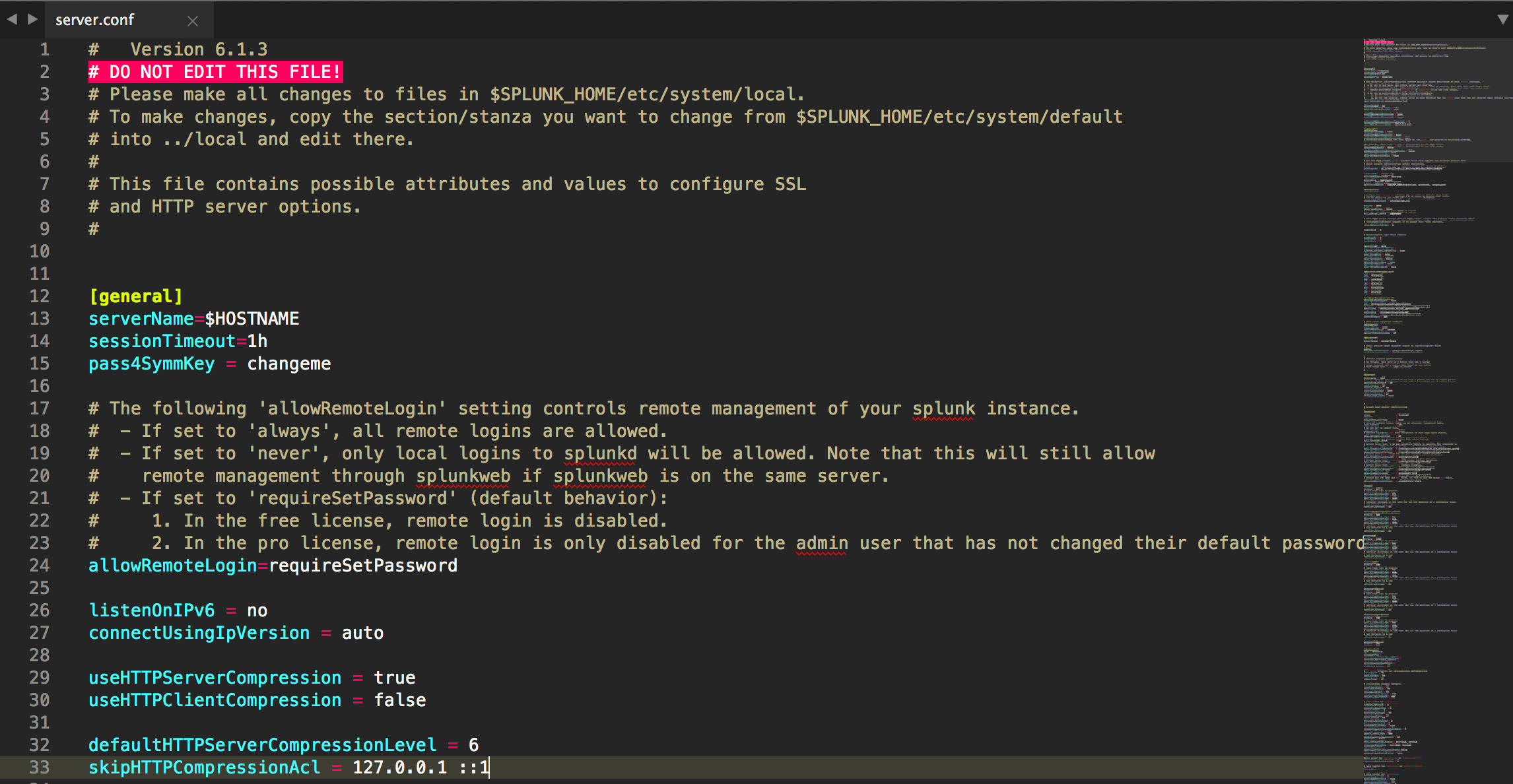

Sublime Text is awesome! But, there’s no great way to get syntax highlighting for a Splunk .conf file… until now!
It works with Sublime Text 2 & 3!
- Install it from Package Control – search for
Splunk Conf File Syntax Highlighting
- Clone the repo
cd sublime-splunk-conf-highlighting
cp splunk-conf.tmLanguage ~/Library/Application\ Support/Sublime\ Text\ 2/Packages/user/splunk-conf.tmLanguage
cp splunk-conf.tmLanguage ~/Library/Application\ Support/Sublime\ Text\ 3/Packages/user/splunk-conf.tmLanguage
Patterns are used to identify some part of a file.
Patterns used by this package:
^# DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE\\!$– marks any lines as invalid if they are# DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE!^#.*$– marks any lines that start with#as a comment^\\[.*\\]$– marks any line starting with[and ending with]as a stanza^[\\w+\\.\\-\\:]+– marks the beginning of a line as a conf key; defined by any whitespace, alphanumeric,-or:characters=– marks any=as an equals sign
Patterns have 3 main attributes:
match(or,beginandend): regex patternsname: aTextMatelanguage grammar group,comment.linefor an inline commentcomment: a comment about the pattern
- This TextMate Language Grammars guide is really helpful for figuring out what name to use for each rule.
There are 2 important files here:
-
splunk-conf.YAML-tmLanguage– TheAAAPackageDevpackage compiles this to the following, this YAML file is much easier to use -
splunk-conf.tmLanguage– This is a TextMate language definition file in XML format. SublimeText uses this format, it’s a necessary evil. -
Install package control if you haven’t already
-
cmd + shift + P (Mac) or ctrl + shift + P (Windows)
- Install package
- AAAPackageDev
-
Open
splunk-conf.YAML-tmLanguage -
cmd + B should update
splunk-conf.tmLanguage, make a small change and see if it worked. If not, play with your build system settings under Tools -> Build System -
During development you’ll need to constantly copy the
splunk-conf.tmLanguageinto your Sublime Text package folder, like so:cp splunk-conf.tmLanguage ~/Library/Application\ Support/Sublime\ Text\ 3/Packages/user/splunk-conf.tmLanguage -
If something doesn’t seem to update, quit & reopen Sublime Text and it should work.
 https://github.com/shakeelmohamed/sublime-splunk-conf-highlighting
https://github.com/shakeelmohamed/sublime-splunk-conf-highlighting